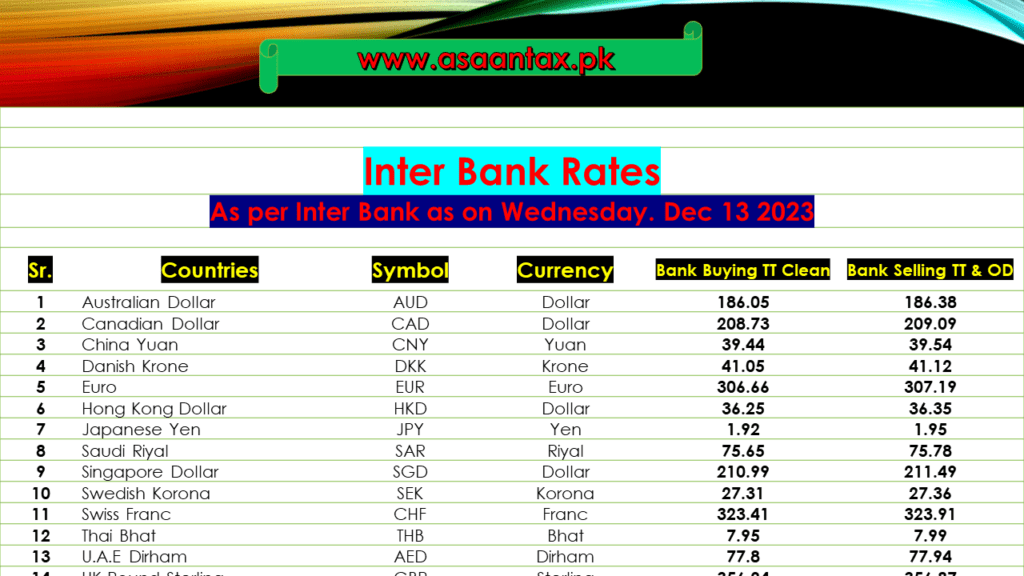
Inter Bank Rate as on 13-Dec-2023, also known as the interbank exchange rate or simply the interbank rate, refers to the interest rate at which banks lend to and borrow from one another in the financial markets. This rate serves as a benchmark for a wide range of financial transactions and influences the overall cost of borrowing in the economy.
Here are key points to understand about the interbank rate:
- Lending Among Banks:
- The interbank rate reflects the interest rate at which banks are willing to lend funds to each other. Banks engage in these transactions to manage their short-term liquidity needs.
- Short-Term Transactions:
- Interbank lending typically involves short-term transactions, often ranging from overnight to a few weeks. Banks use these transactions to meet reserve requirements or address temporary mismatches between their assets and liabilities.
- Risk-Free Rate:
- The interbank rate is considered a relatively low-risk or risk-free rate because it involves transactions between financial institutions. The rate is influenced by central bank policies, market demand and supply, and perceptions of credit risk among banks.
- Influence on Interest Rates:
- The interbank rate has a significant impact on broader interest rates in the economy. It serves as a reference point for setting interest rates on various financial products, including loans, mortgages, and short-term securities.
- Benchmark for Forex Markets:
- In the context of foreign exchange (forex) markets, the interbank exchange rate represents the rate at which major banks conduct currency transactions with each other. This rate is often used as a benchmark for currency conversion and pricing in international financial markets.
- Central Bank Influence:
- Central banks play a crucial role in influencing interbank rates through monetary policy. By setting policy rates, such as the overnight lending rate, central banks can guide interbank rates and, in turn, influence economic conditions.
- Daily Fixing:
- Interbank rates are often set or fixed on a daily basis. The fixing process involves determining the reference rate for the day based on transactions and quotes provided by participating banks.
Understanding the interbank rate is essential for financial institutions, traders, and policymakers as it directly impacts the cost of funds in the banking system and influences broader economic conditions. It is a key indicator in financial markets and is closely monitored by participants for insights into market liquidity and credit conditions.
- The interbank rate is the interest rate at which banks lend and borrow funds from each other in the financial market. It is a crucial benchmark that influences various financial instruments and transactions.
Factors Influencing Inter Bank Rates:
- Central Bank Policies: Central banks play a significant role in influencing interbank rates through monetary policy decisions, such as adjusting the policy interest rates.
- Economic Conditions: Interbank rates are influenced by broader economic conditions, including inflation, economic growth, and employment levels.
- Market Demand and Supply: The rates are also affected by the demand and supply of money in the interbank market.
Importance of Inter Bank Rates:
- Benchmark: Interbank rates serve as a benchmark for setting interest rates on various financial products, such as loans, mortgages, and other credit instruments.
- Financial Markets: They play a crucial role in determining the cost of borrowing for financial institutions and impact overall liquidity in the financial markets.
- Forex Market: In the context of foreign exchange, interbank rates influence the pricing of currency pairs in the forex market.
To obtain the Inter Bank Rate in Pakistan on December 13, 2023, you may check with official financial institutions, central banks, or reputable financial news sources that provide real-time and historical data on interbank rates. Keep in mind that these rates can vary based on the specific currency pairs and the financial institution involved.
